Arracacha
- Womenscorner Desk
- October 8, 2020
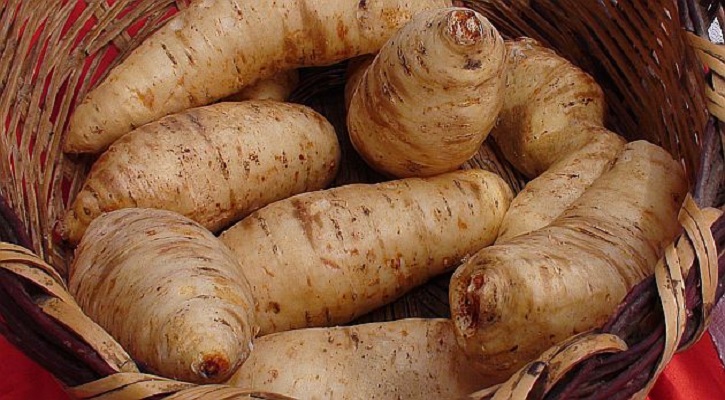
Arracacha (Arracacia xanthorrhiza) may be a vegetable originally from the Andes, somewhat intermediate between the carrot and celery root. Its starchy taproot may be a popular food item in South America where it's a serious commercial crop.
Being a South American plant, its commonest names are in either Spanish or Portuguese, the 2 most spoken languages therein continent. The name arracacha (or racacha) was borrowed into Spanish from Quechua raqacha, and is employed within the Andean region. The plant is additionally called apio or apio criollo ("Creole celery") in Venezuela and Puerto Rico, zanahoria blanca ("white carrot") in Ecuador, and virraca in Peru.
Read More : Creamy Garlic Chicken Breasts
Its Portuguese names are usually derived from the plant's similarity to other documented vegetables and roots. it's referred to as either mandioquinha ("little cassava") or batata-baroa ("baroness potato") in most regions of Brazil, but other common names in certain regions of that country include batata-salsa (“parsley potato”), batata fiúza ("trustworthy potato"), cenourinha-branca ("little white carrot"), and cenourinha-amarela or just cenoura-amarela ("little yellow carrot" or just "yellow carrot"), among others.
It is sometimes called white carrot in English, but that name properly belongs to white sorts of the common carrot. 100 grams of arracacha provide about 100 calories, 26g of which are dry matter, 23g being carbohydrate, and fewer than 1g of protein. The plant is rich in calcium, having fourfold the maximum amount as potatoes.
The yellow cultivar contains substantial amounts of carotenoid pigments, precursors to vitamin A , to the purpose that excessive consumption of arracachas may cause yellowing of the skin, a condition that's not considered to be harmful.
Read More : Arame Seaweed